Project Title: AI-Supported Early Disease Detection System for Tomato Greenhouses Using Multi-Spectral Imaging
This Project will be carried out by ARTECS (Ankara Üniversitesi Technopark) and Wellztech (ODTÜ Teknopark) between 01 November 2025 and 30 October 2027.
Supported by: TÜBİTAK 1501 Program
Project Overview
In modern soilless tomato cultivation, plant diseases often spread rapidly and remain invisible to the naked eye during their early stages. These undetected infections can cause up to 30% annual yield losses. Our project introduces a next-generation AI-driven early warning system designed to detect diseases before they become visible, helping farmers protect their crops, reduce costs, and minimize chemical usage.
Using hyperspectral imaging combined with deep learning algorithms (GANs, Autoencoders, and classification models), the system automatically identifies anomalies in both visible and infrared spectrums. Over time, data from hyperspectral cameras will be leveraged to develop cost-efficient custom sensors, making the solution more affordable and scalable for commercial greenhouses.
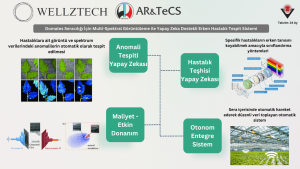


Key Features & Benefits
- Early Disease Detection: Identifies plant stress and diseases at their earliest stage, preventing spread and crop loss.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Reduces the need for pesticides, supporting greener production and aligning with the EU Green Deal.
- Cost-Effective Technology: Custom low-cost sensor sets replace expensive hyperspectral cameras.
- Autonomous Operation: Compatible with existing greenhouse trolleys, capable of automated movement and real-time monitoring.
- Data-Driven Insights: Provides growers with disease mapping and real-time alerts for faster interventions.
- Safer Work Environment: Minimizes chemical exposure for workers.
- Local Innovation: Develops domestic AI models and sensor technology, reducing technological dependency.
Expected Impacts
This innovative system has the potential to:
- Increase yield and quality in tomato production.
- Lower chemical (pesticide) usage
- Lower operational costs and improve labor efficiency.
- Contribute to sustainable food security and climate resilience.
- Serve as a foundation for future R&D in agricultural robotics and smart farming.


.

